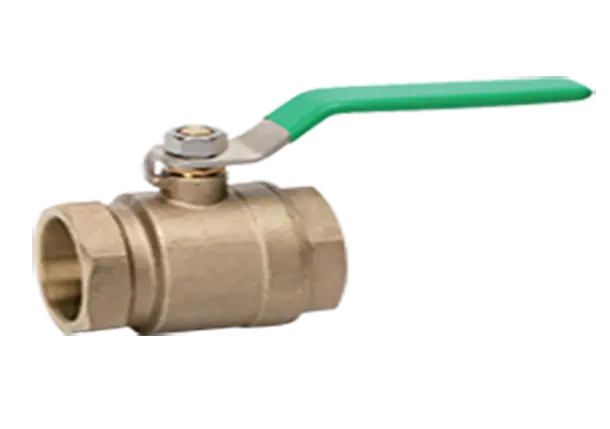
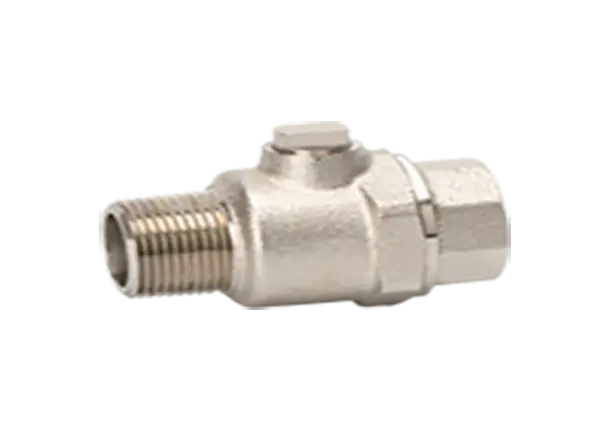
Understanding the Working Principle of Expansion Ball Valves
Expansion ball valves play a crucial role in various industries, allowing for smooth regulation of fluid flow and preventing leaks. Understanding their working principle is fundamental for ensuring efficient operations and optimal performance. In this blog, we will delve into the intricacies of expansion ball valves, exploring their purpose, structure, and functionality.
What is an Expansion Ball Valve?
Expansion ball valves are mechanical devices used to regulate fluid flow through a pipe or duct system. They are specifically designed for applications requiring precise control over fluid movement, temperature, and pressure. These valves excel at handling expansion and contraction caused by temperature variations, making them an ideal choice for various industries such as HVAC, chemical, and oil and gas.
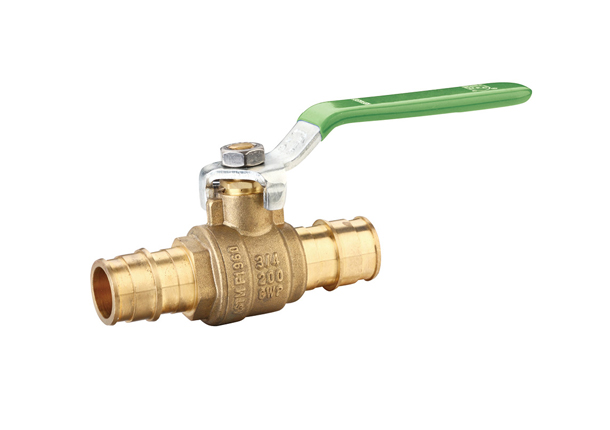

Components and Structure of Expansion Ball Valves
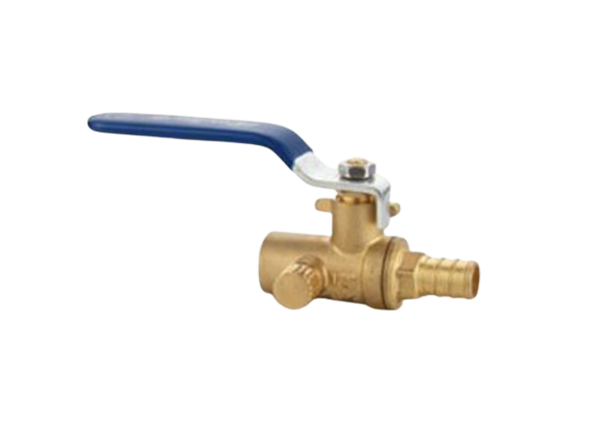
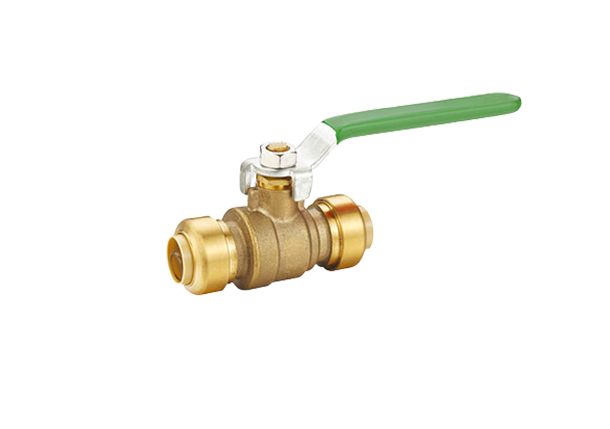
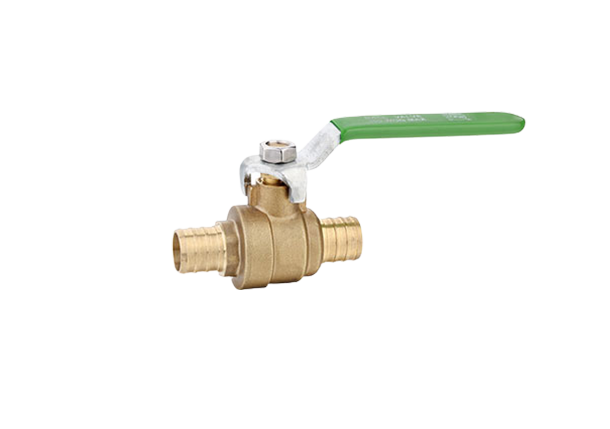
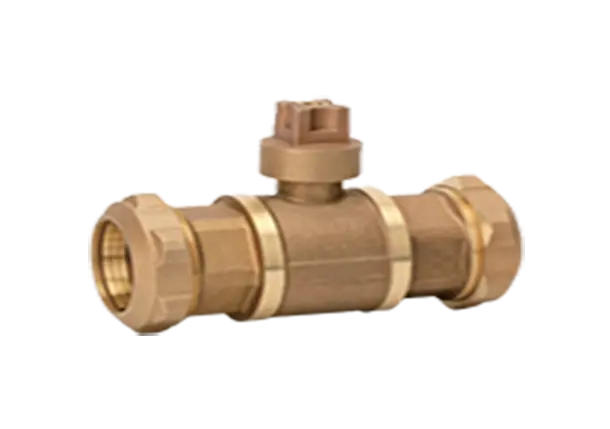
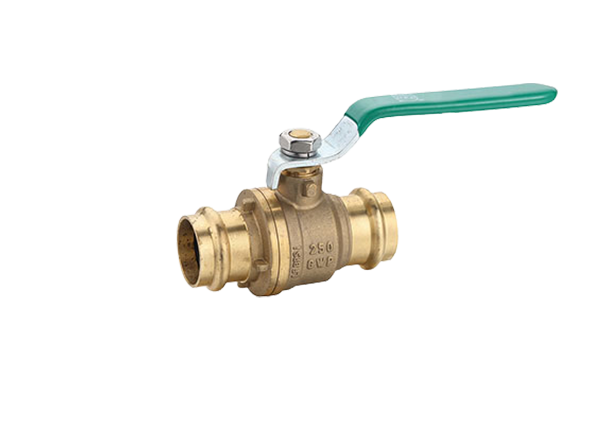
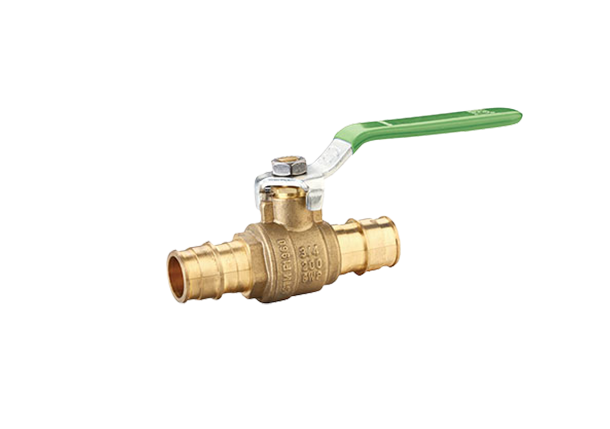
Expansion ball valves consist of several key components, including a spherical hollow ball, a stem, a seat, and a sealing mechanism. The ball is situated within the valve body and, when rotated, controls the flow. The stem is responsible for transmitting motion to the ball and is connected to the handle or actuator. The seat provides a sealing surface where the ball rests, ensuring airtight closure when in the closed position. The sealing mechanism is vital to prevent leaks and can be made of various materials compatible with the fluid being controlled. The valve body is usually constructed from durable materials such as stainless steel or brass, offering resistance against corrosion and extending the lifespan of the valve.
Working Mechanism of Expansion Ball Valves
Expansion ball valves operate on a quarter-turn principle, which means that the ball rotates 90 degrees to control fluid flow. In the closed position, the ball blocks the flow path, preventing the fluid from passing through. When the valve is fully open, the ball aligns with the pipe, allowing unrestricted flow. The position of the ball can be adjusted at any angle between fully open and fully closed, providing precise control and modulation.
One of the unique characteristics of expansion ball valves is their ability to compensate for thermal expansion and contraction. As temperature changes, materials in the valve expand or contract. The expansion ball valve is specifically designed to handle these changes by allowing the ball to rotate freely, maintaining a tight seal in the closed position and facilitating smooth operation without leakage when open.
Applications and Benefits of Expansion Ball Valves
The versatile nature of expansion ball valves makes them suitable for a wide range of applications. Their ability to handle thermal expansion and contraction makes them particularly effective in HVAC systems, where temperature fluctuations are common. These valves are also widely used in chemical and petrochemical industries, power plants, and oil and gas refineries.
The benefits of expansion ball valves include precise control over fluid flow, reduced leak risks, and durability. With their quarter-turn operation, these valves can quickly and efficiently manipulate fluid flow, minimizing energy loss and optimizing system performance. Their robust construction ensures resistance to harsh environments, enhancing reliability and extending the lifespan of the valve.
Expansion ball valves are essential for many industries, offering excellent control over fluid flow, temperature, and pressure regulation. Understanding their working principle and structure is vital for successful implementation. With their ability to compensate for thermal expansion and contraction, expansion ball valves ensure seamless operations and help maintain a safe and efficient working environment.
Different Carbo Valves For Sale